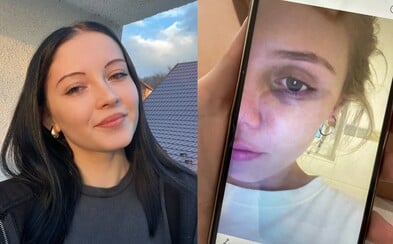
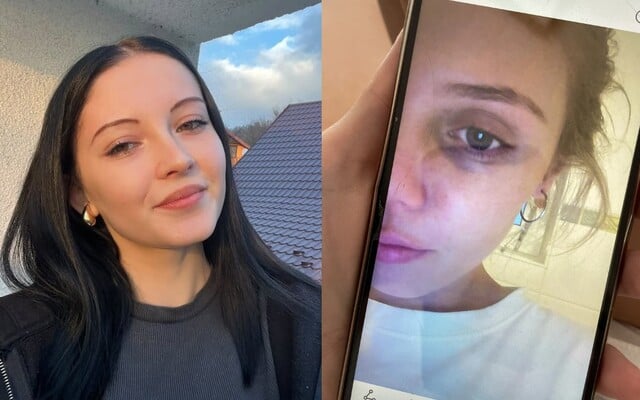
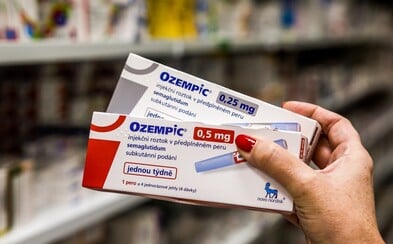
 Ozempic can cause vision loss. A new study has shown a link between the drug and eye problems
Ozempic can cause vision loss. A new study has shown a link between the drug and eye problems
Ozempic can cause vision loss. A new study has shown a link between the drug and eye problems
Ozempic can cause vision loss. A new study has shown a link between the drug and eye problems
Valerian, Ashvaganda or CBD? We Looked Into Which Nutritional Supplements Can Help You With Stress And Anxiety
Natural does not mean safe, but they can help with mild anxiety. We can find a number of over-the-counter nutritional supplements in pharmacies - but do they work?
If problems persis, please contact administrator.

In recent years, the amount of prescribed antidepressants and sleeping pills has risen dramatically. Only last year, the number doubled. Mental health has been deteriorating since the beginning of the pandemic. However, long-term use of antidepressants or prescription drugs can lead to side effects and addictions.
Because of this, the interest in natural over-the-counter nutritional supplements, has been growing. Most of them contain a combination of herbs and natural extracts, to which many manufacturers attribute miraculous effects - achieving mental and physical well-being, reducing fatigue and exhaustion, increased capability to cope with stress or overall increase in strength of the body. CBD or Ashvaganda are extremely popular.
Some of these supplements can actually alleviate the symptoms of anxiety, stress or even mild depression, but the evidence is with many of these relatively weak. So we decided to find out what science was saying.
Nutritional supplements fall under the Food Act - therefore, their manufacturers only have to prove that they are not harmful, when they are placed on the market. As they are not drugs, it is not required to test their effectiveness.
When choosing supplements keep in mind that natural does not automatically mean safe. Some herbal extracts can cause unwanted side effects, especially when combined with other medicine. In addition, as with food, you should be careful about who you buy it from and what the supplement's ingredients are. It is forbidden to make false claims about their health effects on the packaging of nutritional supplements, i.e. provide any information about prevention, treatment or healing. You should not trust a product that does so.
Valerian
Valerian extract can be found in a number of nutritional supplements against anxiety or stress, usually in combination with other herbs, such as passion fruit, honeydew or magnesium. In particular, it is the root that is harvested from this herb, which is first dried and then crushed. Its main substance is silica, which gives the plant its special aroma (its delicate smell is said to attract cats). You buy it either dried in the form of tea, tablets or drops.
Valerian is used mainly for its mild sedative effects, making it beneficial not only for anxiety and stress relief, but also for improving the quality of sleep. Although there is insufficient evidence of its effectiveness from clinical trials, according to the Committee for Herbal Medicinal Products of the European Medicines Agency (EMA), its effectiveness has been reliably proven. EMA concluded, that based on long-term use, valerian silica can be used to relieve mild symptoms of mental distress and to promote sleep.

A 2020 meta-analysis of 60 studies found that valerian is a safe and effective sleep-promoting herb and can help prevent sleep-related disorders.
Scientific studies explain the effectiveness of valerian through its interaction with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps regulate the transmission of nerve impulses in the brain and central nervous system. Valeric acid is said to suppress the breakdown of GABA in the brain, thus helping induce a sense of peace and well-being. Diazepam or Xanax, which are prescription drugs, work this way.
Rarely, side effects such as nausea and abdominal cramps, as well as dizziness or headaches may occur. A recommended dosage of valerian is 300-600 mg per day.
Ashvaganda
Ashvaganda, also known as "Indian ginseng" or "winter cherry", has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for more than 2,500 years. Alternative medicine classifies it as an "adaptogenic plant", said to improve the resistance of the human body to stress.
The effects of Ashvaganda are mainly associated with the support of the function of the endocrine glands of the adrenal glands, which release the hormones cortisol and adrenaline. Ashvaganda could help with "adrenal fatigue" as a result of which these hormones are disrupted. You can take 1,000 mg a day.

The results of studies to date, which confirm the positive effects of this plant, are promising, but there is still very little research. We looked at two randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies. Thus, neither the participants in the experiment nor the doctor knew which group received the placebo and which Ashvaganda.
In a 2019 study, 60 stressed adults received either a placebo or 240 mg of Ashvaganda extract once a day. Study participants subjectively reported stress and anxiety using the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale. In the end, those who took Ashvaganda reported a "significant decrease" in anxiety levels.
Similar results were confirmed by a 2012 study of 64 people with chronic stress. The group receiving 300 mg of asvaganda for two months showed a significant reduction in cortisol levels compared to the placebo group. In contrast, a new clinical study from 2021, in which 40 men and 40 women used asvaganda for 8 weeks, showed virtually no effects of this plant. More research is therefore needed to confirm its effectiveness.
L-tryptophan
L-tryptophan is an essential amino acid that the human body cannot produce on its own and must be supplemented from the diet (found in fish, meat, nuts or bananas, for example). It is the basic substance for the production of serotonin ("happiness hormone") - a chemical compound that is involved in the transmission of information between nerve cells. Its deficiency can manifest itself in depressive states and feelings of anxiety.

Psychiatrists point out that the use of L-tryptophan may help in the clinical treatment of depression and personality disorder. It is usually used in combination with antidepressants.
Its positive effect on reducing anxiety and stress was also confirmed by a 2019 study. But despite the growing number of quality studies, the psychiatric community is still skeptical about L-tryptophan. The recommended daily intake for an 80-kilogram adult is 278 to 476 mg.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral necessary for the correct functioning of important vitals and enzymes. Some of them are part of the activity of nerves and muscles, others regulate blood sugar and blood pressure. Magnesium is presented as a prevention of diabetes, cardiovascular disease and migraine, but these claims are not substantiated by solid evidence. The health benefits of magnesium supplements have very little support among scientists, says biochemist and writer Graham Lawton his publication This Book Could Save Your Life: The Real Science of Living Longer Better.
The vast majority of people can absorb enough magnesium from their diet (for example, it can be found in leafy vegetables, nuts, legumes, yogurts and cereals) and its supplementation in the form of nutritional supplements is therefore unnecessary, according to some scientists. Serious magnesium deficits are rare and tend to affect patients with chronic illnesses. We should not take more than 310-420 mg per day (recommended average intake varies, depending on gender and age).
A few studies (1, 2) suggest, that magnesium may be beneficial in the treatment of mental illness, but according to researchers, there are no high-quality randomised studies to confirm that it can alleviate the symptoms of anxiety and stress.
CBD
CBD, i.e. cannabidiol, is definitely one of the most discussed (and at the same time most expensive) supplements for stress, anxiety, but also depression or panic. CBD is said to increase the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain and thus deepen the ability to control emotional responses. As a result, it can induce mental well-being, promote concentration, memory or even relieve pain and help relieve indigestion. It is used in the cosmetics industry to smooth out wrinkles or soothe the skin. You can find it on the market in the form of drops, cream, oil or oral spray.

Studies conducted on laboratory mice have shown that CBD could lead to a reduction of fear-related neurones. Some human studies have shown a positive effect of CBD on social anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder or depressive states. One randomized, double-blind study showed positive effects of CBD on patients with schizophrenia. However, more comprehensive research has highlighted insufficient evidence.
Extensive research conducted by the acclaimed journal The Lancet Psychiatry has examined 83 studies that have looked at the use of CBD and THC in the treatment of mental illness. Most of the studies were of poor quality and included only a small number of participants who were followed for a short of amount time.
A recent study from 2020 warns that it is dangerous to label CBD as a "miracle drug", especially given the list of possible toxic side effects. "Currently, one cannot be sure what is in the product. From this point of view, CBD is not safe and its risks outweigh the benefits," the scientists write. They also did not rule out the possible addictiveness of the substance.
CBD can actually make your anxiety worse. Researchers from 2017 found that almost 70% of all CBD products had false information on the packaging and contained significant amounts of THC, which can have adverse psychoactive effects - not to mention that you could end up with a positive drug test.
If problems persis, please contact administrator.